Multigenerational Living: The Rise of Extended Family Homes
Multigenerational living is experiencing a resurgence in popularity as families seek practical and affordable solutions that foster stronger bonds and more quality time together. With changing demographics and cultural shifts, the demand for homes that can accommodate multiple generations has increased significantly. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of multigenerational living, its benefits, and the various types of housing options available. Whether you are considering this lifestyle for your own family or assisting clients in finding the perfect multigenerational home, this article will provide valuable insights and guidance.
What is Multigenerational Housing?
Multigenerational housing, also known as multigen or next-gen homes, refers to residences that accommodate two or more generations living together under one roof. This living arrangement can include parents, grandparents, adult children, and grandchildren. Multigenerational homes provide separate living spaces and privacy for each generation, allowing for a harmonious coexistence.
The Changing Landscape of Multigenerational Living
The concept of multigenerational living is not new. In the past, it was the norm for multiple generations to live together, often out of necessity or cultural tradition. However, as society evolved and families became more affluent, the trend shifted towards independent living arrangements. Now, with economic factors, longer life expectancies, and a desire for closer family connections, multigenerational living is once again on the rise.
The Benefits of Multigenerational Living
Multigenerational living offers numerous advantages for families. One of the most significant benefits is the potential for economic efficiency. By sharing expenses, such as mortgage payments, utilities, and household chores, families can reduce financial burdens and achieve greater financial stability. Additionally, multigenerational living fosters strong family ties, provides a support system, and allows for the sharing of caregiving responsibilities. Children also benefit from the wisdom and guidance of grandparents, while older family members enjoy the companionship and assistance of younger generations.
Types of Multigenerational Housing
There are various types of housing options designed to accommodate multigenerational living. These include:
1. Multigenerational Single-Family Homes
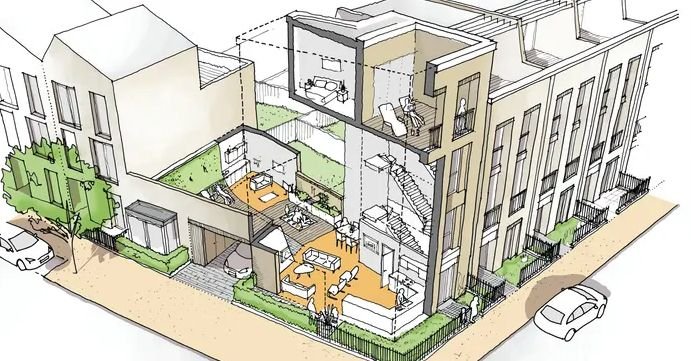
Multigenerational single-family homes are traditional houses that are modified or purpose-built to accommodate multiple generations. These homes often feature separate living spaces, such as attached or detached accessory dwelling units (ADUs), granny flats, or mother-in-law suites. They may also have additional bedrooms, bathrooms, or kitchens to provide each generation with their own private space.
2. Multigenerational Condo Units
Multigenerational condo units are specifically designed or renovated condominium buildings that cater to the needs of multiple generations. These units may have separate entrances, private living areas, and shared common spaces. Developers are increasingly recognizing the demand for multigenerational condos and are incorporating features that promote privacy and flexibility in their designs.
3. Multigenerational Townhouses
Multigenerational townhouses are an excellent option for families seeking a balance between privacy and togetherness. These multi-level homes typically offer separate living areas on different floors, allowing each generation to have their own space. Townhouses can be customized to include additional bedrooms, bathrooms, or even separate entrances to accommodate multigenerational living.
4. Multigenerational Apartments
Multigenerational apartments are becoming more prevalent, particularly in urban areas. These apartment complexes feature larger units with multiple bedrooms and bathrooms, providing space for extended family members to live together comfortably. Some apartments may also offer communal areas or amenities that encourage family interactions and socialization.
The Rise of Multigenerational Living
The rise of multigenerational living can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, changing demographics, including an increasing aging population and diverse cultural backgrounds, have influenced the demand for extended family homes. Additionally, economic factors, such as rising housing costs and the need for dual incomes, have made multigenerational living an attractive option for many families. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as families seek safety, support, and companionship during uncertain times.
Design Considerations for Multigenerational Homes
When designing or selecting a multigenerational home, certain factors should be taken into consideration to ensure the comfort and well-being of all family members. These include:
1. Privacy and Separate Living Areas
Privacy is crucial in multigenerational homes. Each generation should have their own private living spaces, including bedrooms, bathrooms, and possibly separate entrances. This allows for personal space and independence while fostering a sense of belonging and togetherness within the larger household.
2. Universal Design and Accessibility
Multigenerational homes should be designed with universal design principles in mind. This ensures that the home is accessible and safe for individuals of all ages and abilities. Features like wider doorways, step-free entrances, grab bars, and lever-style door handles can enhance accessibility and make the home more accommodating for older family members or those with mobility challenges.
3. Flexibility and Future Adaptability
Flexibility and adaptability are key considerations when designing a multigenerational home. As family dynamics change over time, the home should be able to accommodate evolving needs. This may involve flexible floor plans that can be easily modified or repurposed, such as converting a home office into an additional bedroom or creating a separate living area for an aging parent.
4. Common Spaces for Family Bonding
While privacy is essential, it’s equally important to have common spaces that encourage family bonding and social interaction. These can include shared living rooms, dining areas, outdoor spaces, or recreational areas where family members can come together, share meals, engage in activities, and create lasting memories.
oUR FINAL THOUGHTS
Multigenerational living is a growing trend that offers numerous benefits for families seeking closer connections, shared responsibilities, and financial stability. Whether it’s a multigenerational single-family home, condo unit, townhouse, or apartment, there are housing options available to suit different family sizes and preferences. When considering a multigenerational home, it’s crucial to prioritize privacy, accessibility, flexibility, and common spaces for family bonding. By embracing the concept of multigenerational living, families can create a supportive and enriching environment where generations thrive together.
Remember, multigenerational living is not just a housing choice; it’s a lifestyle that promotes stronger family ties and enhanced well-being. Embrace the benefits of multigenerational living and discover the joy of sharing your home with multiple generations.
Rate this article
Researched and Written by
Peter Jonathan Wilcheck
American Management Services (www.goamx.com)
and
Chris Tambakis
Centieme Luxury Condos (www.centiemecondos.com